Tunnel lining is a critical aspect of underground construction, ensuring structural stability, water tightness, and long-term durability. Understanding the construction process, materials, and best practices can help engineers and project managers mitigate risks and maintain high-quality standards. In this article, we break down the tunnel lining construction process, highlight common challenges, and provide practical solutions to ensure successful project execution.
1. Preparation: Laying the Groundwork for Success
The first step in any tunnel lining project is careful preparation, which sets the foundation for safe and efficient construction. Key activities include:
Site Survey & Geotechnical Investigation: Understanding soil conditions, groundwater levels, and rock types helps in selecting appropriate lining methods and materials.
Design Verification: Confirming structural and hydraulic design parameters to ensure the lining can withstand anticipated loads and pressures.
Equipment & Material Planning: Ensuring timely availability of formwork, concrete, reinforcement, and curing materials to avoid delays.
Tip: Using 3D tunnel modeling software can help visualize lining segments and anticipate complex geometries, reducing errors during construction.
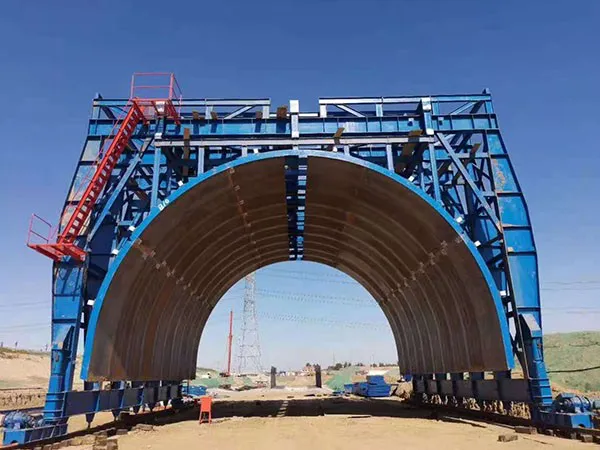
Suggested Image: Site preparation diagram showing bore alignment and excavation zones.
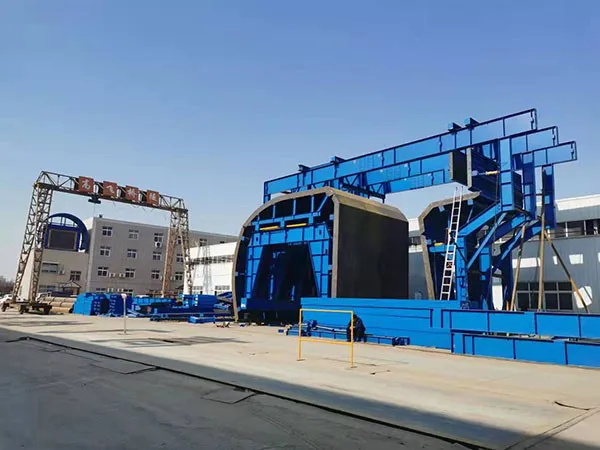
2. Formwork Installation: Building the Framework
Formwork or templates are essential for shaping the tunnel lining. Depending on the project, steel, timber, or modular formwork may be used.
Template Positioning: Proper alignment and anchoring are critical to avoid dimensional errors.
Reinforcement Placement: Steel rebar is installed according to design specifications, ensuring structural strength and crack resistance.
Quality Checks: Prior to pouring concrete, verify correct spacing, alignment, and stability of templates.
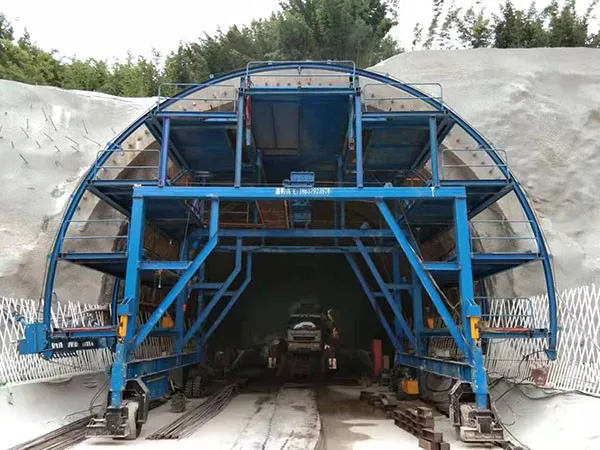
Suggested Image: Formwork and reinforcement setup inside an under-construction tunnel.
3. Concrete Casting: Ensuring Durability and Strength
Concrete pouring is the most sensitive phase in tunnel lining construction. Best practices include:
Mix Design Compliance: Use high-performance concrete tailored for tunnel environments, considering compressive strength, workability, and water tightness.
Continuous Pouring: Avoid cold joints by ensuring uninterrupted concrete flow.
Vibration & Compaction: Proper consolidation reduces voids and enhances structural integrity.
Challenges to Watch For:
Segment Collapse: Insufficient support or poor-quality concrete can lead to temporary or permanent collapse.
Leakage: Improper sealing or mix design can cause water infiltration, especially in high groundwater conditions.
Suggested Image: Concrete pouring with vibrating equipment inside a tunnel lining section.
…
For more detailed information on tunnel lining construction technology, please click to visit: https://www.gf-bridge-tunnel.com/a/blog/tunnel-lining-construction-process-explained.html