Vibration motors are devices that generate mechanical vibrations for a variety of applications, such as haptic feedback in devices, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics. There are several types of vibration motors, each with distinct characteristics, designs, and applications.
Types of Vibration Motors
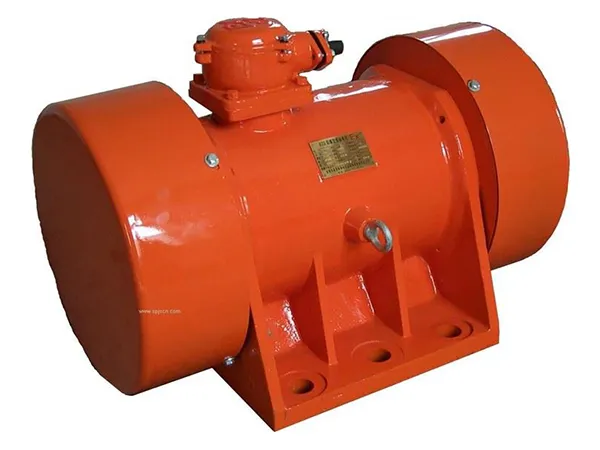

Eccentric Rotating Mass (ERM) Motors
Description: ERM motors are DC motors with an unbalanced weight attached to the shaft. When the motor rotates, the centrifugal force generated by the offset weight causes the motor to vibrate.
Applications: Widely used in mobile phones, pagers, wearable devices, and other small handheld gadgets for haptic feedback.
Advantages: Simple design, cost-effective, easy to control the vibration intensity by varying the speed of rotation.
Disadvantages: The vibration is not uniform due to the rotating mass.
Linear Resonant Actuators (LRA):
Description: LRAs consist of a magnetic mass suspended by a spring, which oscillates when an AC signal is applied. They are tuned to resonate at a specific frequency, providing a strong vibration at a particular resonance.
Applications: Used in smartphones, tablets, gaming controllers, wearables, and other devices requiring precise haptic feedback.
Advantages: Faster response time, better energy efficiency, and more precise control over vibrations than ERM motors.
Disadvantages: More complex control circuitry is required, and they are typically more expensive than ERM motors.
Coin Vibration Motors:
Description: These are a type of ERM motor that is flat and coin-shaped. The eccentric mass is embedded in a circular housing, making it compact and easy to integrate into slim devices.
Applications: Commonly used in portable devices like smartphones, smartwatches, and fitness bands.
Advantages: Compact size, low power consumption, easy to mount.
Disadvantages: Limited vibration strength due to their small size.
Brushless DC Vibration Motors:
Description: These motors use a brushless DC motor design, where the rotation of a magnet induces vibration without physical brushes. The vibration mechanism is similar to ERM but with higher efficiency and durability.
Applications: Industrial equipment, automotive applications, and more demanding environments requiring long life and reliability.
Advantages: Longer lifespan, lower maintenance, higher efficiency, and better control.
…
More detailed information about vibration motor types can be found at: https://www.zexciter.com/en/a/news/vibration-motors-types.html



